First degree price discrimination aggressive price discrimination that directly targets a customer s ability to pay more such as the size and revenue of a corporation. It does not result in deadweight losses so no economic welfare is lost.

Is first degree price discrimination efficient.

1st degree price discrimination examples. Reservation price for the first unit is 147 150 3 1 and so on. Examples of price discrimination. Optimal output under price discrimination.
Also known as perfect price discrimination first degree price discrimination involves charging consumers the maximum price that they are willing to pay for a good or service. The bidder takes the information of the highest price which they are willing to pay from the consumer and accordingly sells the product to the highest bidder. It is simply an attempt to charge different prices to different customers for the same product.
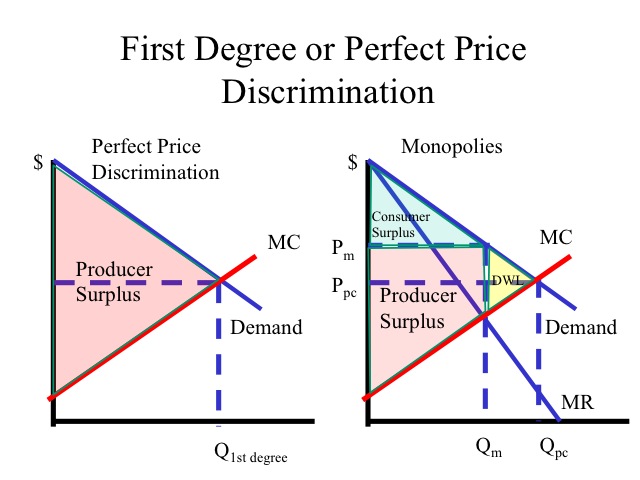
Here consumer surplus is entirely captured by the firm. First degree price discrimination an attempt to charge different prices to different customers for the same product. First degree price discrimination or perfect discrimination is the highest level of price discrimination in which each unit of production is sold at the maximum price that the consumer is willing to pay for that specific unit.
All consumers pay the same price. In practice a consumer s maximum willingness to pay is difficult to determine. An auction occurs when consumers bid up to the maximum amount they are willing to pay.
Monopolies are particularly prone to implement first degree price discrimination if left unregulated. An auction is said to be an example of first degree price discrimination. Marc bourreau tpt lecture 01.
When there is no price discrimination and a single price is charged from each customer the profit maximizing output for a firm facing a downward sloping demand curve occurs at a point at which its marginal revenue is equal to its marginal cost. A closer example of first degree discrimination is online auction like ebay. Lipsey and chrystal 2007.
This is not true price discrimination but uses the same principles finding customers with more inelastic demand. First degree price discrimination. Its use is widespread such as first and standard class.
2 2 first degree price discrimination. Customers tend to dislike these schemes and it typically requires a strong market position to implement. In an ideal business world companies would be able to eliminate all consumer surplus through first degree price discrimination.
Has been around ever since people began bartering and exchanging goods. This type of pricing strategy. First degree price discrimination is efficient.
The monopoly sets a price for calls that maximizes consumers surplus. And extracts all the surplus with the subscription price. Price discrimination first degree price discrimination an example of first degree price discrimination results the optimal price is such that p c and f v p intuition.
This petrol station is offering cut price fuel for two days a week.
 Micro 4 8 Price Discriminating Monopoly First Degree Tax Write Offs Knowledge Feelings
Micro 4 8 Price Discriminating Monopoly First Degree Tax Write Offs Knowledge Feelings
 Forum Learn English Fluent Landcollocations With High Fluent Land Vocabulario En Ingles Gramatica Del Ingles Aprender Ingles
Forum Learn English Fluent Landcollocations With High Fluent Land Vocabulario En Ingles Gramatica Del Ingles Aprender Ingles
 Why Colleges Are Like Cable Companies Cable Companies College Financial Planning College Costs
Why Colleges Are Like Cable Companies Cable Companies College Financial Planning College Costs
 Examples Of Price Discrimination Economics Help
Examples Of Price Discrimination Economics Help
![]() First Degree Price Discrimination Policonomics
First Degree Price Discrimination Policonomics
 Montessori Materials Parts Of Speech Grammar Symbol Charts Montessori Materials Montessori Elementary Montessori Lessons
Montessori Materials Parts Of Speech Grammar Symbol Charts Montessori Materials Montessori Elementary Montessori Lessons
 Topic 7 Poster On The Difference Between Phonological Awareness And Phonemic Awareness Phonological Awareness Phonemic Awareness Phonology
Topic 7 Poster On The Difference Between Phonological Awareness And Phonemic Awareness Phonological Awareness Phonemic Awareness Phonology
 Price Discrimination Intelligent Economist
Price Discrimination Intelligent Economist
 3 Main Forms Of Price Discrimination With Diagram
3 Main Forms Of Price Discrimination With Diagram

0 comments:
Post a Comment